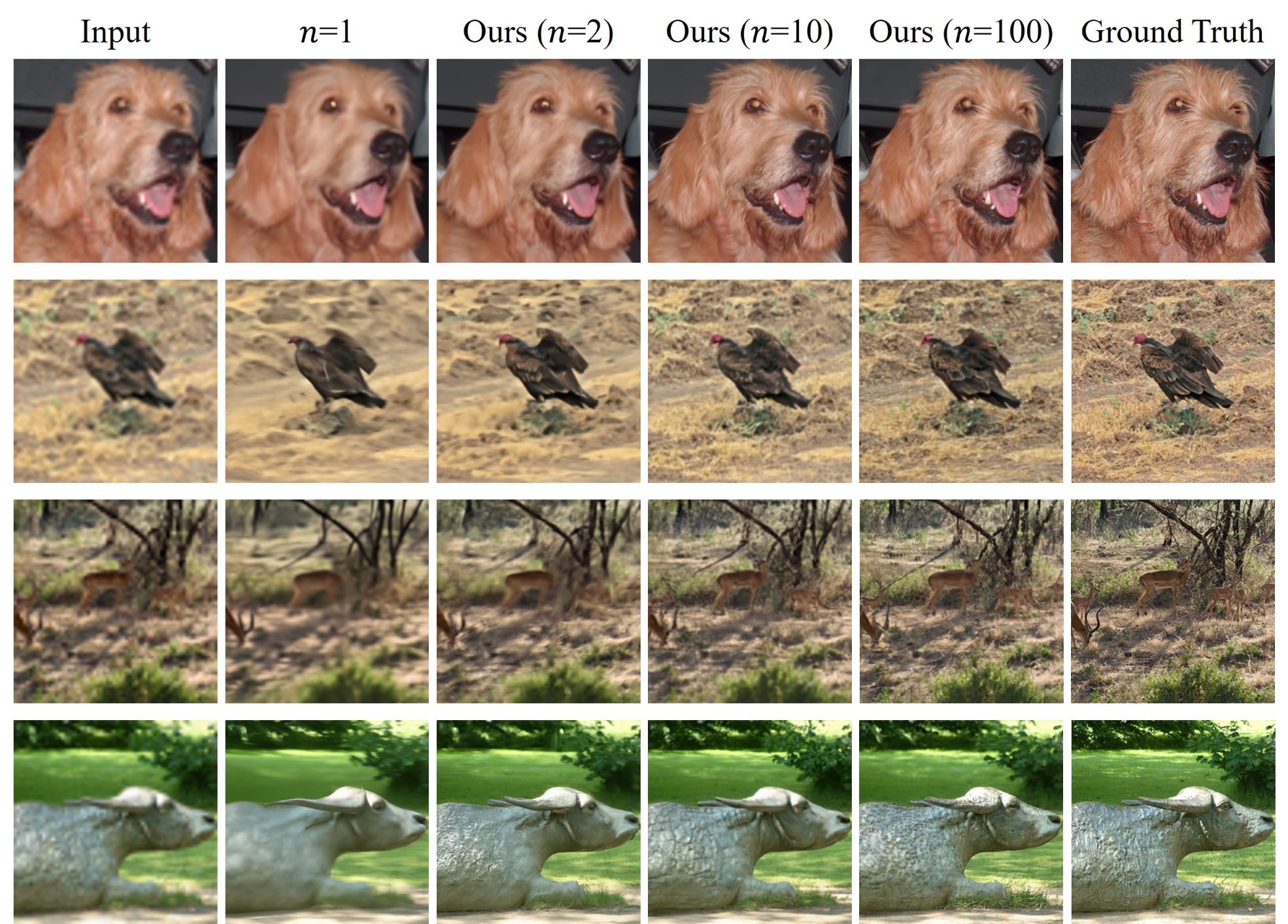

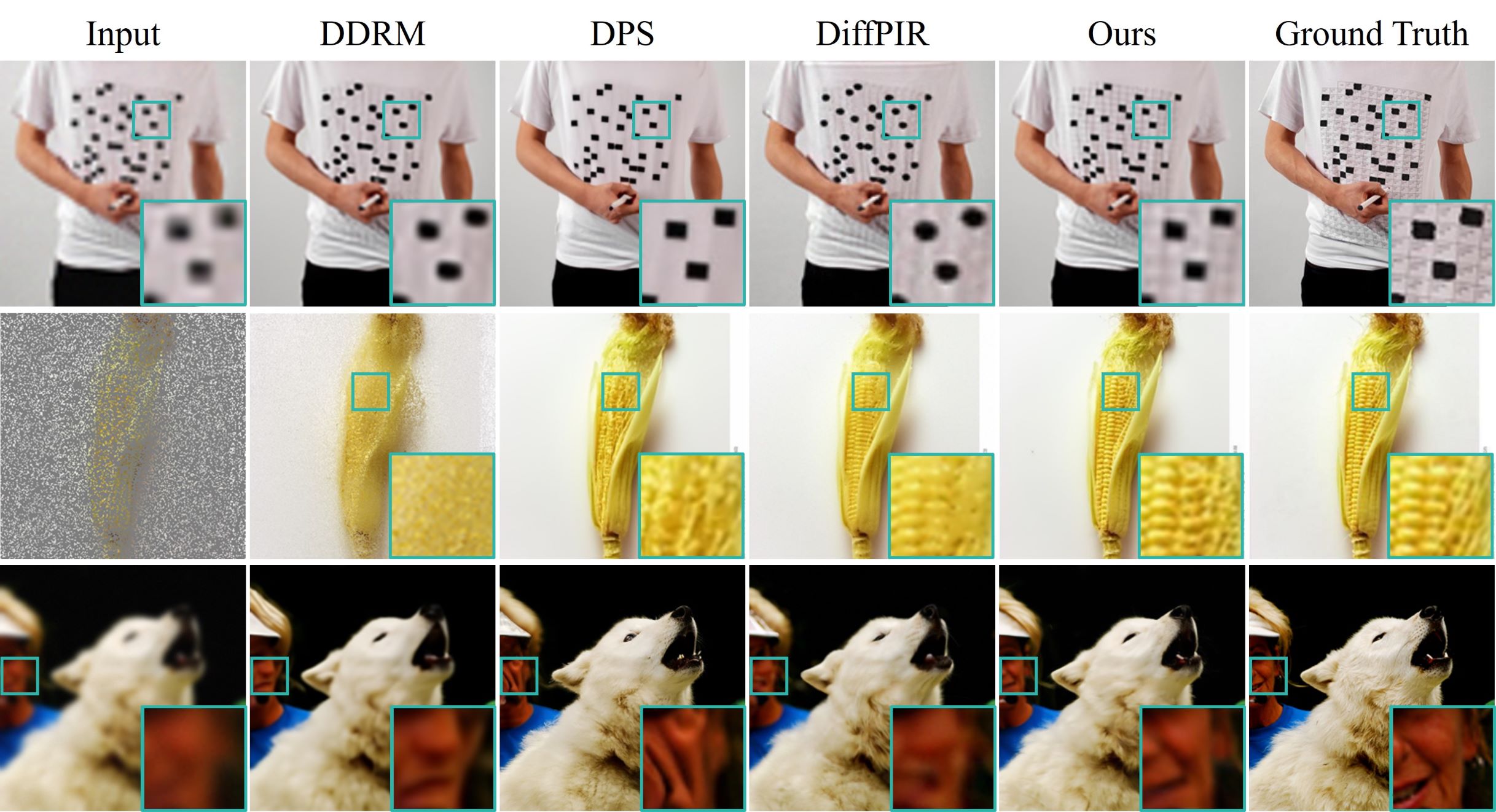
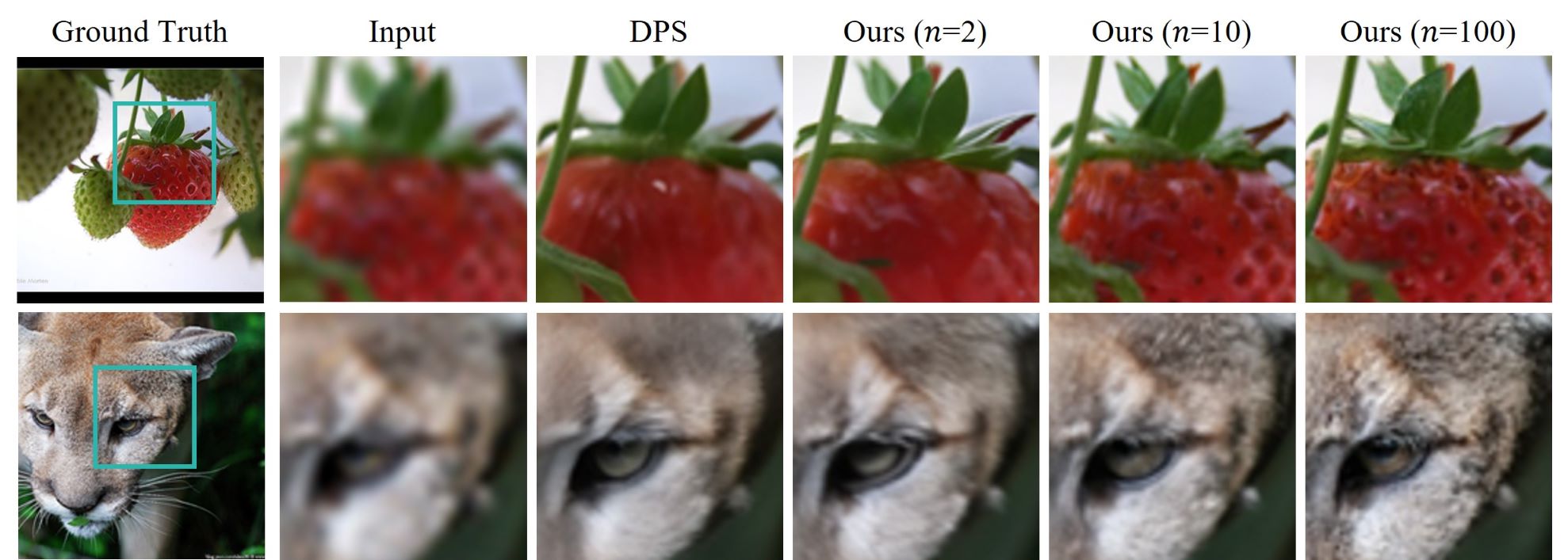
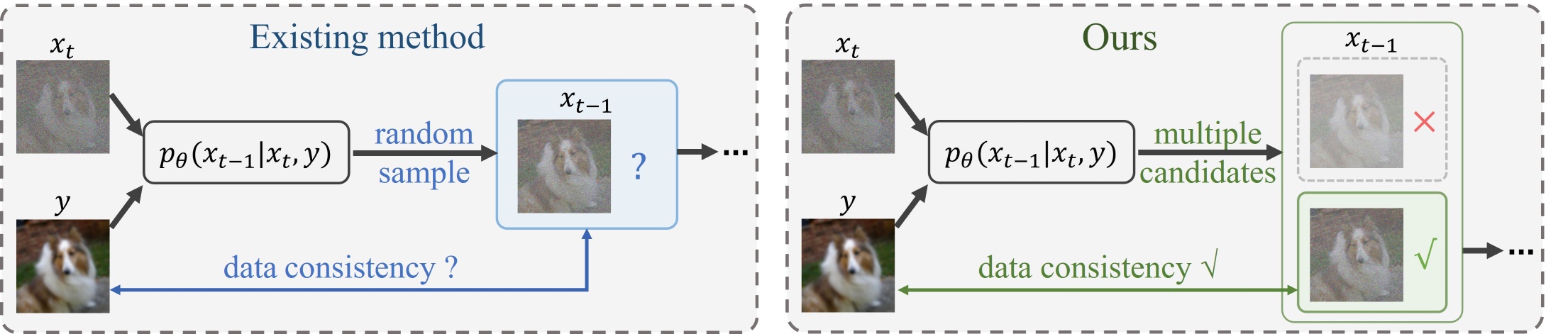
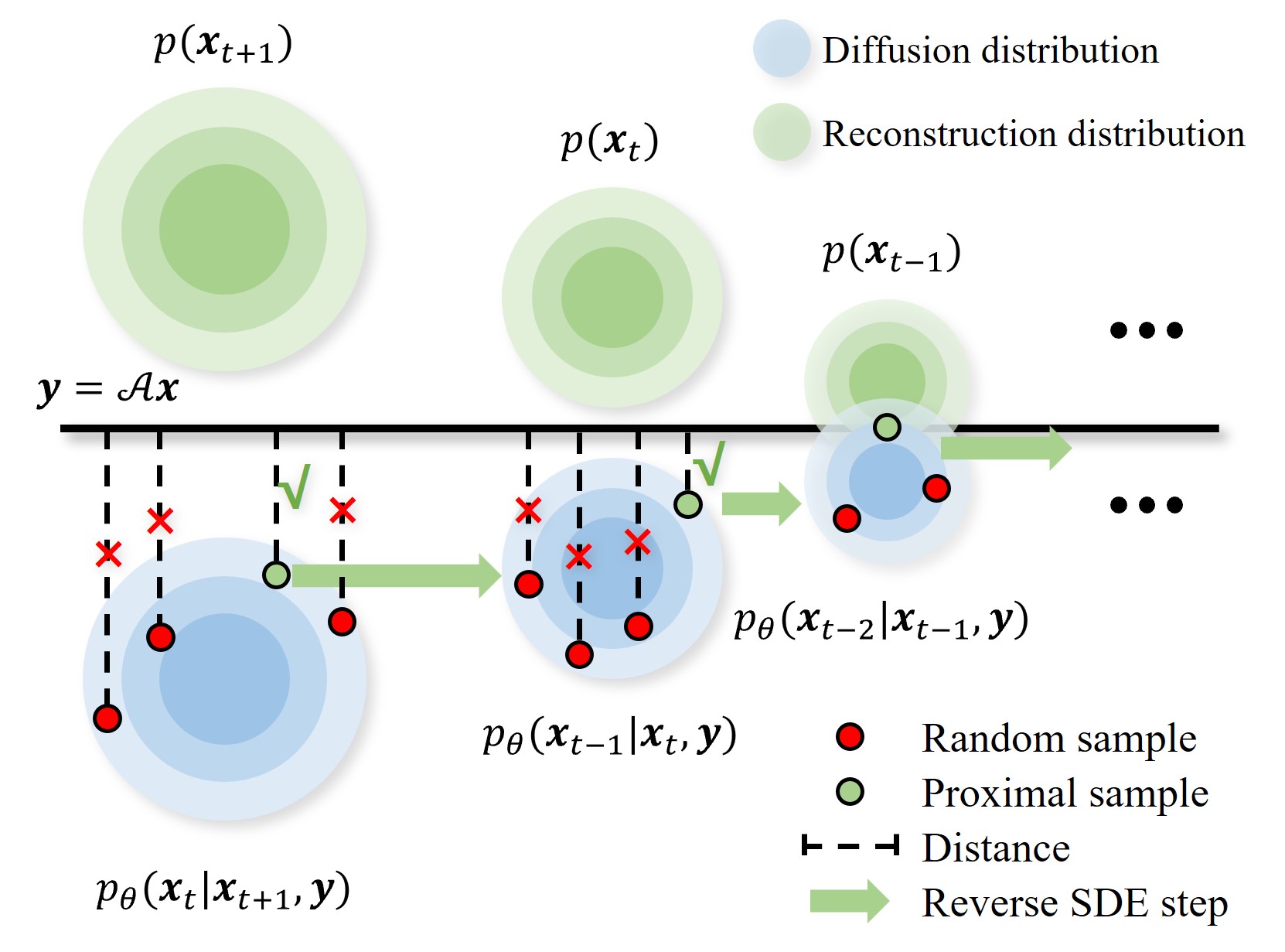
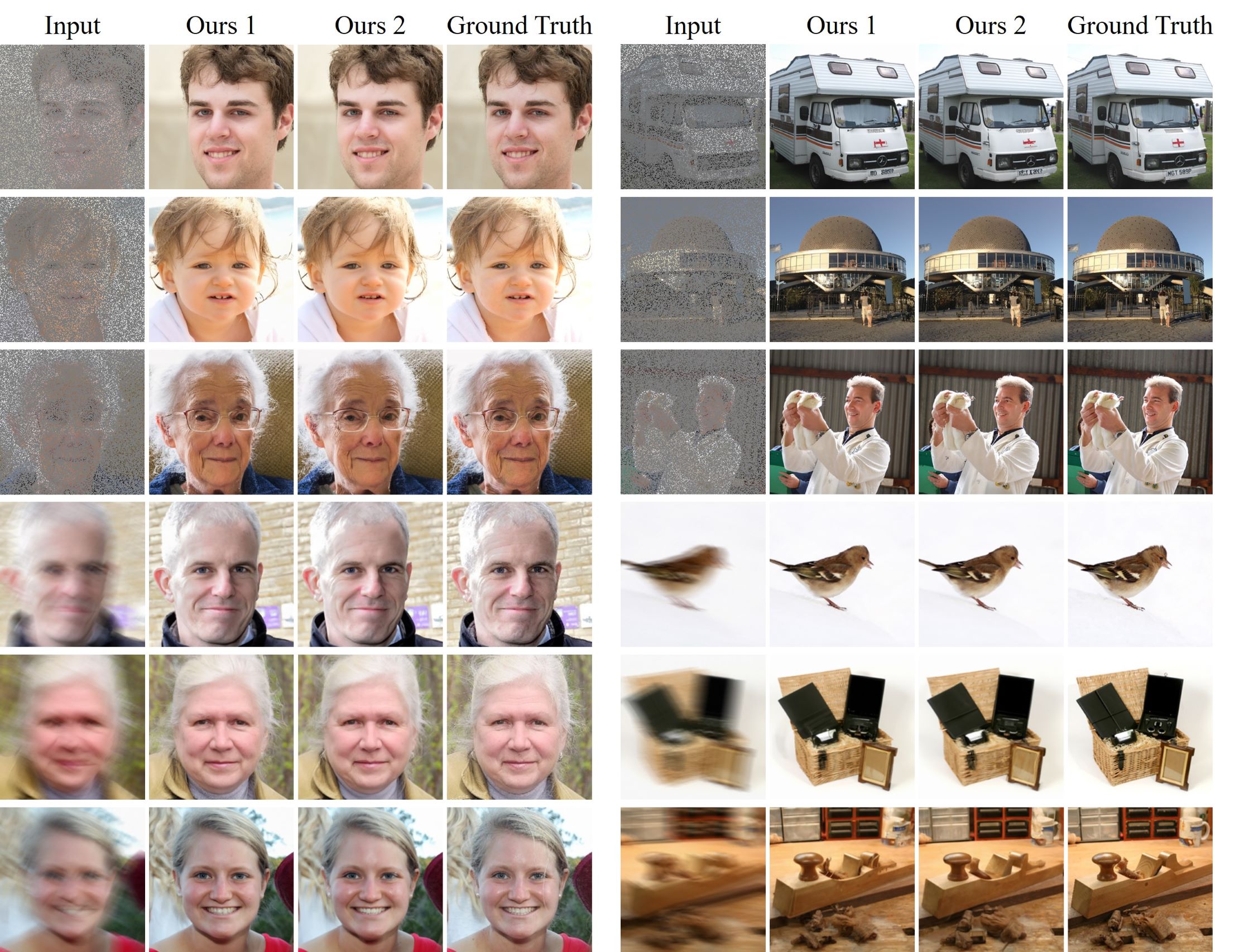
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in generating high-quality samples. Existing diffusion-based image restoration algorithms exploit pre-trained diffusion models to leverage data priors, yet they still preserve elements inherited from the unconditional generation paradigm. These strategies initiate the denoising process with pure white noise and incorporate random noise at each generative step, leading to over-smoothed results. In this paper, we introduce a refined paradigm for diffusion-based image restoration. Specifically, we opt for a sample consistent with the measurement identity at each generative step, exploiting the sampling selection as an avenue for output stability and enhancement. Besides, we start the restoration process with an initialization combined with the measurement signal, providing supplementary information to better align the generative process. Extensive experimental results and analyses validate the effectiveness of our proposed approach across diverse image restoration tasks.


We thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and feedback. We extend our gratitude to Mengxi Xie from SJTU and Linrui Dai from CQU for their constructive suggestions on the figures, although we ultimately did not adopt them. This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.1082204112364), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No.62106161), and the Sichuan University Luzhou Municipal Government Strategic Cooperation Project (No.2022CDLZ-8).
@inproceedings{wu2024diffusion,
title={Diffusion Posterior Proximal Sampling for Image Restoration},
author={Wu, Hongjie and He, Linchao and Zhang, Mingqin and Chen, Dongdong and Luo, Kunming and Luo, Mengting and Zhou, Ji-Zhe and Chen, Hu and Lv, Jiancheng},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia},
pages={214--223},
year={2024}
}